
Mårtensson, "Core-Level Binding Energies in Metals," J. Lide, (Ed.) in Chemical Rubber Company handbook of chemistry and physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 81st edition, 2000. Ley, Eds., Photoemission in Solids I: General Principles (Springer-Verlag, Berlin) with additional corrections, 1978. Burr, "Reevaluation of X-Ray Atomic Energy Levels," Rev. They are tabulated elsewhere on the WWW (reference 4) and in paper form (reference 5). The data are adapted from references 1-3. I am grateful to Gwyn Williams (Jefferson Laboratory, Virginia, USA) who provided the electron binding energy data. The binding energies are quoted relative to the vacuum level for rare gases and H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, and Cl 2 molecules relative to the Fermi level for metals and relative to the top of the valence band for semiconductors. All values of electron binding energies are given in eV. 1967, 47, 1300.Įlectron binding energies Electron binding energies for silver.

First, determine the formula by balancing the charges.The ionic formula is CaCl₂ Subscripts in the chemical formula indicate the number of atoms. The net overall charge must be 0, so we need 2 Cl ions to balance the charge of 1 Ca ion. Look at the periodic table to find the ionic charges of calcium and chlorine: Balance the charges using the table below:įormula: NaCl Example #2 – calcium and chlorine Look at the periodic table to obtain the ionic charges of sodium and chlorine. Note: All elements in the first column tend to lose 1 valence electrons and form ions with 1+ charge All elements in the 2nd column tend to lose 2 valence electrons and form ions with 2+ charge Example #1 – sodium and chlorine All the negative charges must cancel out all the positive charges in the compound.The overall charge in an ionic compound must be neutral.
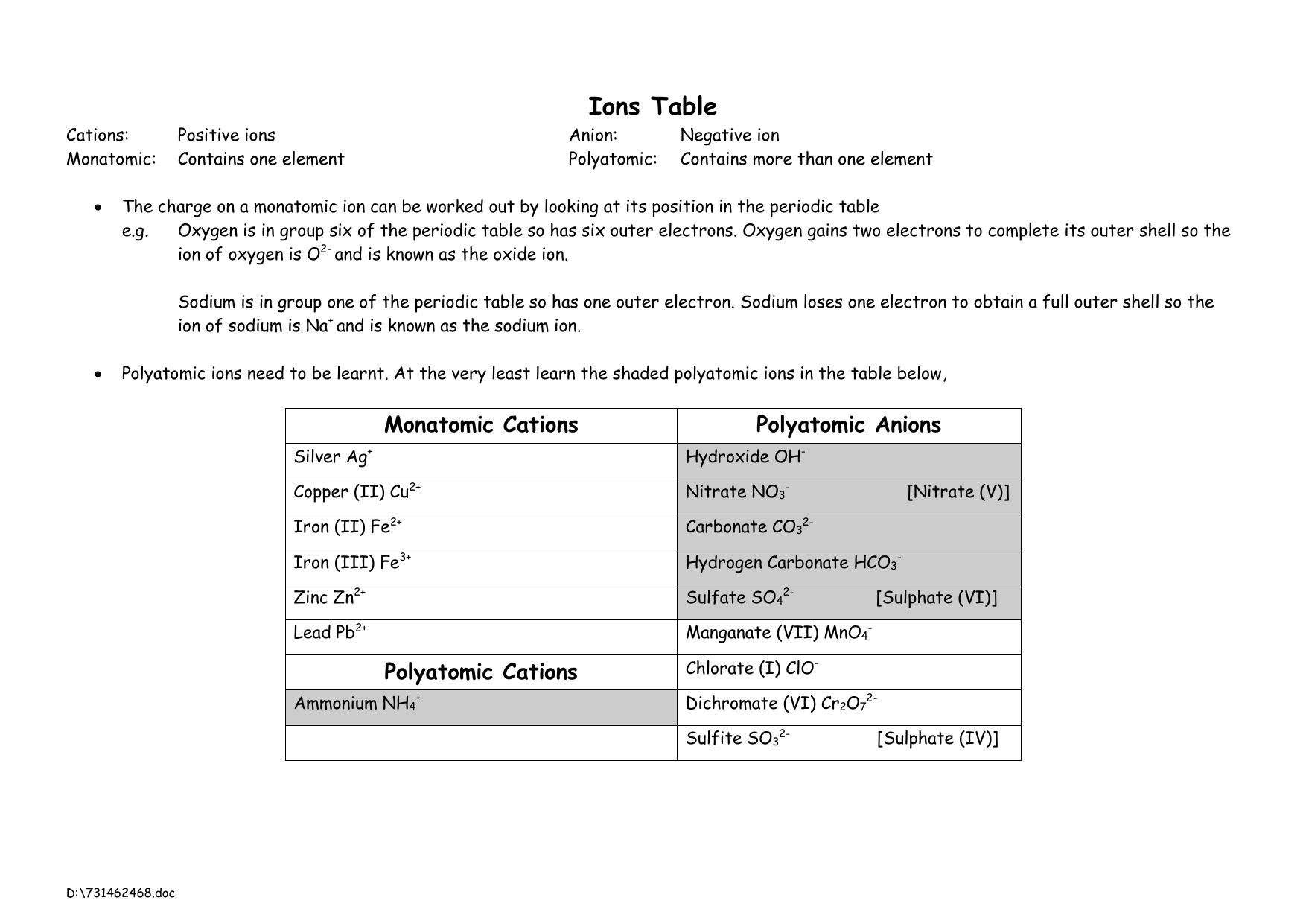
Use the periodic table to determine the charge in an element.
Ag charge silver how to#
It’s important to learn how to balance the charges in ionic compounds The bond that is formed between two oppositely charged ions is called an ionic bond.When the cations and anions come close together, they experience an attraction due to their opposite charges.The atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion – called an anion.The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion – called a cation.Non-metals tend to gain electrons from metals.Metals tend to lose electrons to non-metals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
